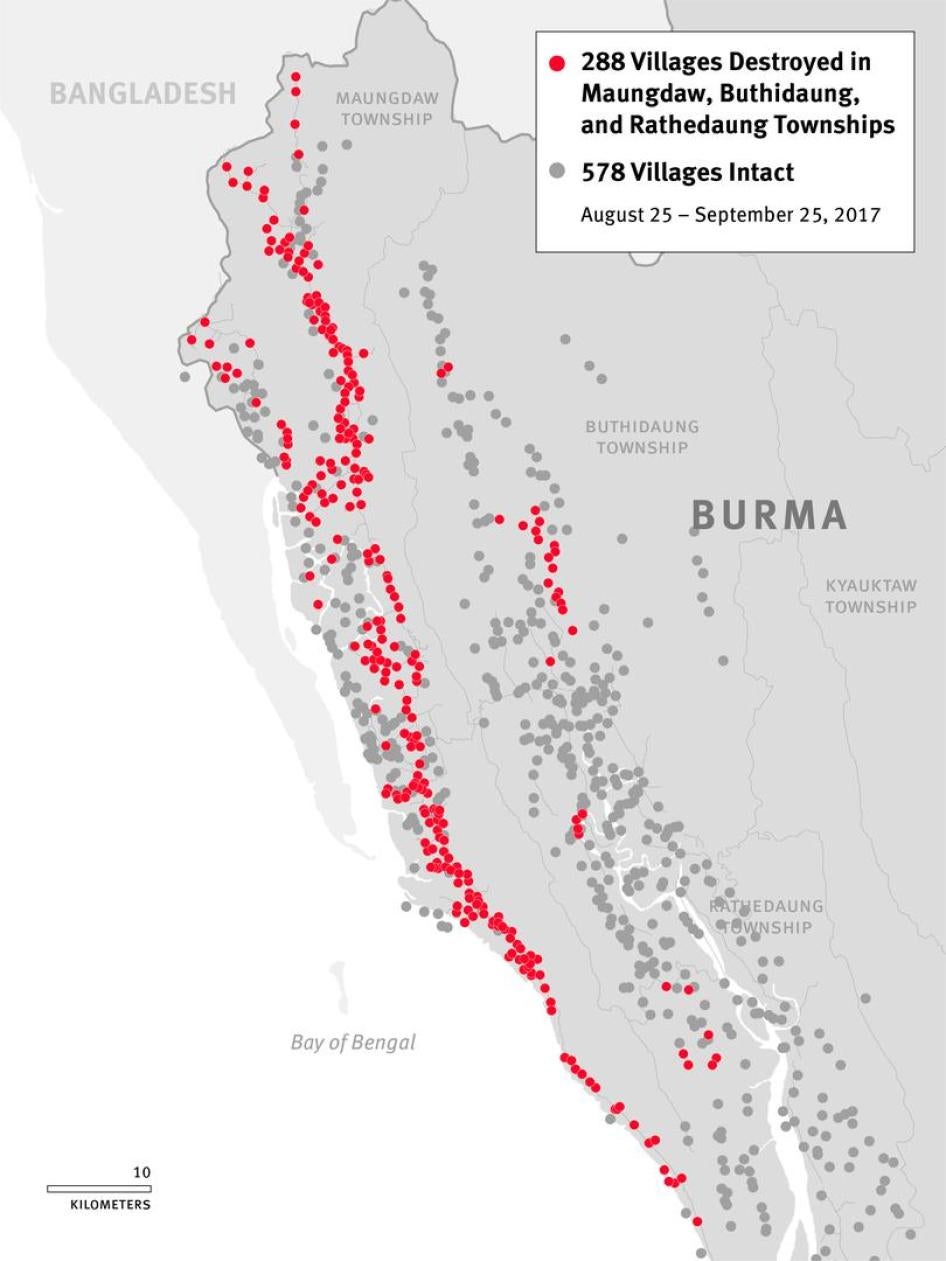
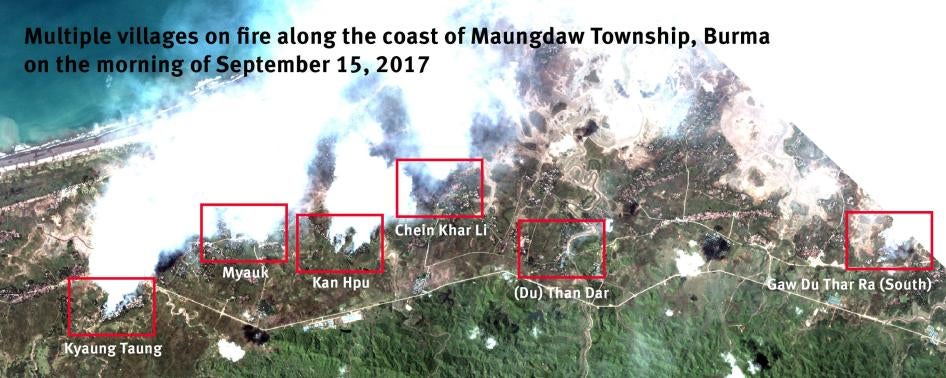
(New York) – Newly released satellite images reveal that at least 288 villages were partially or totally destroyed by fire in northern Rakhine State in Burma since August 25, 2017, Human Rights Watch said today. The destruction encompassed tens of thousands of structures, primarily homes inhabited by ethnic Rohingya Muslims.
Analysis of the satellite imagery indicates both that the burnings focused on Rohingya villages and took place after Burmese officials claimed security force “clearance operations” had ceased, Human Rights Watch said. The imagery pinpoints multiple areas where destroyed Rohingya villages sat adjacent to intact ethnic Rakhine villages. It also shows that at least 66 villages were burned after September 5, when security force operations supposedly ended, according to a September 18 speech by State Counselor Aung San Suu Kyi. The Burmese military responded to attacks on August 25 by the Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army (ARSA) with a campaign of ethnic cleansing, prompting more than 530,000 Rohingya to flee across the border to Bangladesh, according to the United Nations refugee agency.
“These latest satellite images show why over half a million Rohingya fled to Bangladesh in just four weeks,” said Phil Robertson, deputy Asia director. “The Burmese military destroyed hundreds of Rohingya villages while committing killings, rapes, and other crimes against humanity that forced Rohingya to flee for their lives.”
A total of 866 villages in Maungdaw, Rathedaung, and Buthidaung townships in Rakhine State were monitored and analyzed by Human Rights Watch. The most damage occurred in Maungdaw Township, accounting for approximately 90 percent of the areas where destruction happened between August 25 and September 25. Approximately 62 percent of all villages in the township were either partially or completely destroyed, and southern areas of the township were particularly hard hit, with approximately 90 percent of the villages devastated. In many places, satellite imagery showed multiple areas on fire, burning simultaneously over wide areas for extended periods.
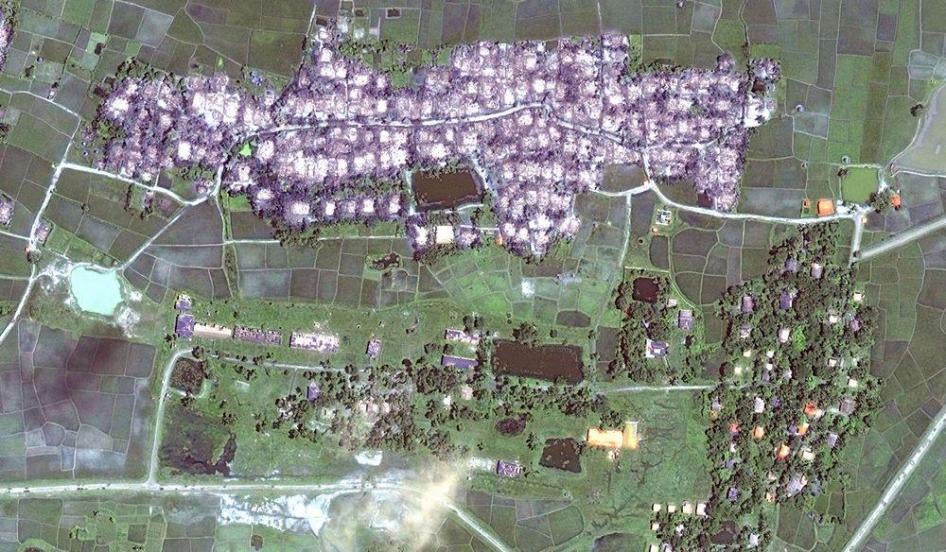
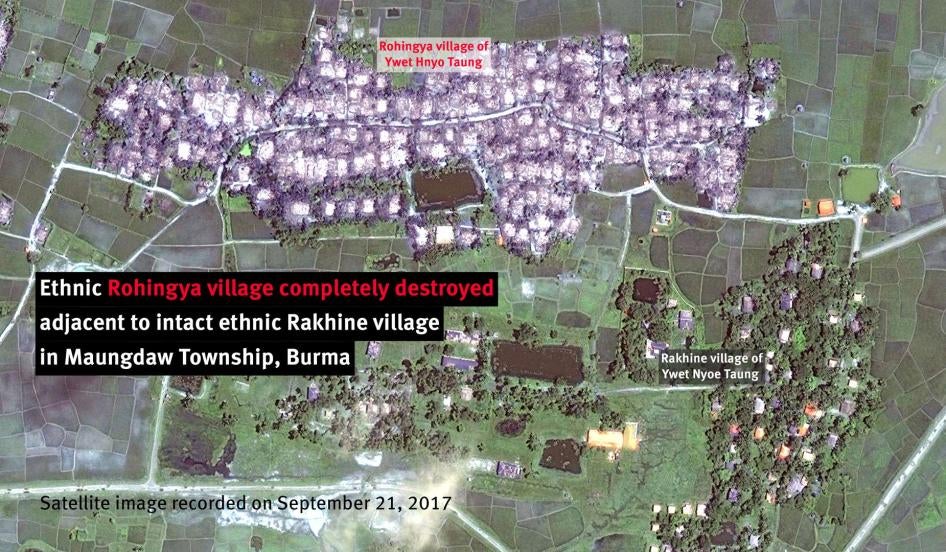
Human Rights Watch found that the damage patterns are consistent with fire. Comparing recent imagery with those taken prior to the date of the attacks, analysis showed that most of the damaged villages were 90 to 100 percent destroyed. Many villages which had both Rohingya and Rakhine residing in segregated communities, such as Inn Din and Ywet Hnyo Taung, suffered heavy arson damage from arson attacks, with known Rohingya areas burned to the ground while known Rakhine areas were left intact.
The Burmese government has repeatedly said that ARSA insurgents and local Rohingya communities were responsible for setting the fires that wiped out their villages, but has offered no evidence to support such claims. Human Rights Watch interviews in Bangladesh with more than 100 refugees who had fled the three townships gave no indication that any Rohingya villagers or militants were responsible for burning down their own villages.
The Burmese government and military has not impartially investigated and prosecuted alleged serious abuses committed against the Rohingya population. UN member countries and international bodies should press the Burmese government to grant access to the UN-mandated fact-finding mission to investigate these abuses. The UN Security Council should also urgently impose a global arms embargo on Burma, and place travel bans and asset freezes on those Burmese commanders responsible for grave abuses. Governments should impose a comprehensive arms embargo against Burma, including prohibiting military cooperation and financial transactions with military-owned enterprises.
“The shocking images of destruction in Burma and burgeoning refugee camps in Bangladesh are two sides of the same coin of human misery being inflicted on the Rohingya,” Robertson said. “Concerned governments need to urgently press for an end to abuses against the Rohingya and ensure that humanitarian aid reaches everyone in need.”